Economic Biology Online Test 9th Science Lesson 23 Questions in English
Economic Biology Online Test 9th Science Lesson 23 Questions in English
Quiz-summary
0 of 135 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
Information
Tnpsc Online Test
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 135 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 135
1. Question
- What is the animal based farming methodologies?
Correct
Explanation
In recent scenario more emphasis is given to the progress of economic aspects of zoology like aquaculture (culture of fish, prawn, crabs, pearl and edible oysters), Vermiculture, apiculture and dairy farming which are gaining more importance as animal-based farming due to their economic and commercial values.
Incorrect
Explanation
In recent scenario more emphasis is given to the progress of economic aspects of zoology like aquaculture (culture of fish, prawn, crabs, pearl and edible oysters), Vermiculture, apiculture and dairy farming which are gaining more importance as animal-based farming due to their economic and commercial values.
-
Question 2 of 135
2. Question
- Which of this cultivation is not dealt with Horticulture?
Correct
Explanation
Horticulture is a branch of agriculture that deals with cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
Incorrect
Explanation
Horticulture is a branch of agriculture that deals with cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
-
Question 3 of 135
3. Question
- What is the origin of the word horticulture?
Correct
Explanation
The word horticulture is derived from the latin words ‘hortus’ meaning garden and ‘colere’ meaning to cultivate.
Incorrect
Explanation
The word horticulture is derived from the latin words ‘hortus’ meaning garden and ‘colere’ meaning to cultivate.
-
Question 4 of 135
4. Question
- Assertion (A): Horticulture is a scientific methodology to improve the quality and growth of plants.
Reasoning(R): Horticulture provides resistance to plants against diseases, insects and stress.
Correct
Explanation
Horticulture is both a science and an art of growing plants with improved growth, quality, yield, and with resistance to diseases, insects, stress etc.
Incorrect
Explanation
Horticulture is both a science and an art of growing plants with improved growth, quality, yield, and with resistance to diseases, insects, stress etc.
-
Question 5 of 135
5. Question
- Which is not a main class of horticulture?
Correct
Explanation
There are four main classes of horticulture: (i) Pomology (fruit farming),(ii) Olericulture (vegetable farming), (iii)Floriculture (flower farming), (iv) Landscape gardening.
Incorrect
Explanation
There are four main classes of horticulture: (i) Pomology (fruit farming),(ii) Olericulture (vegetable farming), (iii)Floriculture (flower farming), (iv) Landscape gardening.
-
Question 6 of 135
6. Question
- What is the meaning of the word pomum in Latin?
Correct
Explanation
The term pomology is derived from the Latin word ‘pomum’ means fruit and ‘logy’ means study.
Incorrect
Explanation
The term pomology is derived from the Latin word ‘pomum’ means fruit and ‘logy’ means study.
-
Question 7 of 135
7. Question
- Which of these are the main factors of pomology?
Correct
Explanation
Pomology deals with development, enhancement of fruit quality, cultivation techniques, regulation of production periods and reduction of production cost of fruits.
Incorrect
Explanation
Pomology deals with development, enhancement of fruit quality, cultivation techniques, regulation of production periods and reduction of production cost of fruits.
-
Question 8 of 135
8. Question
- What is the science of growing vegetables?
Correct
Explanation
Olericulture is the science of growing vegetables.
Incorrect
Explanation
Olericulture is the science of growing vegetables.
-
Question 9 of 135
9. Question
- How many type of vegetable farming is classified?
Correct
Explanation
Vegetable farming can be classified into: i) Kitchen or Nutrition gardening ii) Commercial gardening iii) Vegetable forcing.
Incorrect
Explanation
Vegetable farming can be classified into: i) Kitchen or Nutrition gardening ii) Commercial gardening iii) Vegetable forcing.
-
Question 10 of 135
10. Question
- State some of the vegetables grown in kitchen gardening?
Correct
Explanation
Kitchen gardening is growing of vegetables in small scale at household. e.g. Beans, Cabbage, Lady’s finger, Tomato, Brinjal, Carrot, Spinach etc.
Incorrect
Explanation
Kitchen gardening is growing of vegetables in small scale at household. e.g. Beans, Cabbage, Lady’s finger, Tomato, Brinjal, Carrot, Spinach etc.
-
Question 11 of 135
11. Question
- Which of these statements is true regarding the Uzhavan mobile application?
i) The application is used for the government of Tamil Nadu to gather information on farmers.
ii) This application also provides information on available stock of seeds and fertilizers in local government and private stores.
Correct
Explanation
Government of Tamil Nadu has launched Uzhavan (farmer) mobile application. It can be used by farmers to gather information on farm subsidies, farm equipment’s, crop insurance and weather conditions. It also provides information on available stock of seeds and fertilizers in local government and private stores.
Incorrect
Explanation
Government of Tamil Nadu has launched Uzhavan (farmer) mobile application. It can be used by farmers to gather information on farm subsidies, farm equipment’s, crop insurance and weather conditions. It also provides information on available stock of seeds and fertilizers in local government and private stores.
-
Question 12 of 135
12. Question
- Which of this gardening method involves large scale production of vegetables?
Correct
Explanation
Commercial gardening: It is the production of vegetables in large scale to be sold in markets.
Incorrect
Explanation
Commercial gardening: It is the production of vegetables in large scale to be sold in markets.
-
Question 13 of 135
13. Question
- In which of these places vegetable forcing is used?
Correct
Explanation
Vegetable forcing: It is the method of growing vegetables in buildings, green houses, cold farms or under other artificial growing conditions. It is the most intensive type of vegetable growing. e.g. Cabbage, Tomato, Brinjal etc.
Incorrect
Explanation
Vegetable forcing: It is the method of growing vegetables in buildings, green houses, cold farms or under other artificial growing conditions. It is the most intensive type of vegetable growing. e.g. Cabbage, Tomato, Brinjal etc.
-
Question 14 of 135
14. Question
- Choose the Incorrect statements regarding Greenhouse gardening.
i) A framed structure gardening covered with transparent material.
ii) The crops are grown under partially or fully controlled environmental conditions.
iii) This method is the least growing sector in the agriculture worldwide.
Correct
Explanation
Green House or Poly House: It is a framed structure covered with transparent material to grow crops under partially or fully controlled environmental conditions to get optimum growth and productivity. It is the fastest growing sector in the agriculture worldwide.
Incorrect
Explanation
Green House or Poly House: It is a framed structure covered with transparent material to grow crops under partially or fully controlled environmental conditions to get optimum growth and productivity. It is the fastest growing sector in the agriculture worldwide.
-
Question 15 of 135
15. Question
- Which of the following is not an advantage of greenhouse gardening?
Correct
Explanation
Advantages of Greenhouse
- Disease-free plants can be produced continuously.
- Water requirement of crops is very less.
- Yield is very high compared to outdoor cultivation.
- Limited pesticide is needed.
- It protects plants from uncertain weather.
Incorrect
Explanation
Advantages of Greenhouse
- Disease-free plants can be produced continuously.
- Water requirement of crops is very less.
- Yield is very high compared to outdoor cultivation.
- Limited pesticide is needed.
- It protects plants from uncertain weather.
-
Question 16 of 135
16. Question
- Assertion (A): Floriculture is the art of cultivating flowering and ornamental plants.
Reasoning(R): Traditional flowers, Beautification and value added products are included in floriculture.
Correct
Explanation
Floriculture is the art of cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants in garden for beauty or floristry. It is concerned with growing traditional flowers, cut flowers, bedding plants, foliage potted plants, arboriculture trees, turf grass for beautification and value added products like essential oils, pharmaceutical and nutraceutical compounds.
Incorrect
Explanation
Floriculture is the art of cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants in garden for beauty or floristry. It is concerned with growing traditional flowers, cut flowers, bedding plants, foliage potted plants, arboriculture trees, turf grass for beautification and value added products like essential oils, pharmaceutical and nutraceutical compounds.
-
Question 17 of 135
17. Question
- Which of the following is not grown under the floriculture technique?
Correct
Explanation
Some of the plants by floriculture techniques are, Geraniums (Pelargonium), Busy lizzies (Impatiens), Chrysanthemum and Petunia.
Incorrect
Explanation
Some of the plants by floriculture techniques are, Geraniums (Pelargonium), Busy lizzies (Impatiens), Chrysanthemum and Petunia.
-
Question 18 of 135
18. Question
- Which of the following is true regarding the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana?
Correct
Explanation
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): It is an agricultural crops insurance scheme of Indian government. Under this scheme the central government provides insurance cover and financial assistance to farmers. It was launched on 18th February 2016.
Incorrect
Explanation
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): It is an agricultural crops insurance scheme of Indian government. Under this scheme the central government provides insurance cover and financial assistance to farmers. It was launched on 18th February 2016.
-
Question 19 of 135
19. Question
- What are the uses of flowers?
Correct
Explanation
Uses of flowers
- Flowers are used for decoration purpose.
- They are also used for personal needs and religious and ceremonial offerings.
- They impart color and beauty to the garden.
- They increase country’s economy.
Incorrect
Explanation
Uses of flowers
- Flowers are used for decoration purpose.
- They are also used for personal needs and religious and ceremonial offerings.
- They impart color and beauty to the garden.
- They increase country’s economy.
-
Question 20 of 135
20. Question
- Assertion (A): Landscape horticulture is the study of designing and constructing landscapes.
Reasoning(R): Landscape designing are used for Business firms, public areas and private houses.
Correct
Explanation
Landscape horticulture is the study of designing and constructing landscapes in homes, business firms and public areas to imitate natural scenery.
Incorrect
Explanation
Landscape horticulture is the study of designing and constructing landscapes in homes, business firms and public areas to imitate natural scenery.
-
Question 21 of 135
21. Question
- From which of these organic manures are derived?
Correct
Explanation
Organic manures are predominantly derived from plant debris, animal faeces and microbes. They make the soil fertile by adding nutrients like nitrogen.
Incorrect
Explanation
Organic manures are predominantly derived from plant debris, animal faeces and microbes. They make the soil fertile by adding nutrients like nitrogen.
-
Question 22 of 135
22. Question
- Assertion (A): Animal manure consists of faeces and urine from various domesticated livestock’s.
Reasoning(R): Manures from different animals have the same quality and same applications.
Correct
Explanation
Animal Manure: It consists of faeces and urine from livestocks like cattle, horses, pigs, sheep, chickens, turkeys, rabbits, etc. Manures from different animals have different qualities and different applications.
Incorrect
Explanation
Animal Manure: It consists of faeces and urine from livestocks like cattle, horses, pigs, sheep, chickens, turkeys, rabbits, etc. Manures from different animals have different qualities and different applications.
-
Question 23 of 135
23. Question
- What is the percentage of nitrogen in well decomposed farmyard manure?
Correct
Explanation
Farmyard manure: It is a mixture of cattle dung, urine, litter material and other dairy wastes. On an average well decomposed farm yard manure contains 0.5% Nitrogen, 0.2% available phosphate and 0.5% available potash.
Incorrect
Explanation
Farmyard manure: It is a mixture of cattle dung, urine, litter material and other dairy wastes. On an average well decomposed farm yard manure contains 0.5% Nitrogen, 0.2% available phosphate and 0.5% available potash.
-
Question 24 of 135
24. Question
- Which of these are composed in the sheep and goat manure?
Correct
Explanation
Sheep and Goat manure: It contains higher nutrients than farm yard manure. It contains 3% Nitrogen, 1% phosphorus pentoxide and 2% potassium oxide.
Incorrect
Explanation
Sheep and Goat manure: It contains higher nutrients than farm yard manure. It contains 3% Nitrogen, 1% phosphorus pentoxide and 2% potassium oxide.
-
Question 25 of 135
25. Question
- Which of these is a soil conditioner is produced by natural decomposition of organic matters?
Correct
Explanation
Compost is a soil conditioner as well as a fertilizer that is rich in nutrients. It is produced by natural decomposition of organic matter such as crop residues, animal wastes, and food wastes, industrial and municipal wastes by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
Incorrect
Explanation
Compost is a soil conditioner as well as a fertilizer that is rich in nutrients. It is produced by natural decomposition of organic matter such as crop residues, animal wastes, and food wastes, industrial and municipal wastes by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
-
Question 26 of 135
26. Question
- What are the advantages of using Green manure?
Correct
Explanation
Green manure is obtained by collection and decomposition of green leaves, twigs of trees, field bunds etc. Green manure improves soil structure, increases water holding capacity and decreases soil loss by erosion.
Incorrect
Explanation
Green manure is obtained by collection and decomposition of green leaves, twigs of trees, field bunds etc. Green manure improves soil structure, increases water holding capacity and decreases soil loss by erosion.
-
Question 27 of 135
27. Question
- Which of these plants are decomposed to provide the green manure?
Correct
Explanation
Green manure also helps in reclamation of alkaline soils and reduces weed proliferation. It is manure obtained from un-decomposed green material derived from leguminous plants e.g. Sunhemp (Crotolaria juncea), Dhaincha (Sesbania aculeata), and Sesbania (Sesbania speciosa).
Incorrect
Explanation
Green manure also helps in reclamation of alkaline soils and reduces weed proliferation. It is manure obtained from un-decomposed green material derived from leguminous plants e.g. Sunhemp (Crotolaria juncea), Dhaincha (Sesbania aculeata), and Sesbania (Sesbania speciosa).
-
Question 28 of 135
28. Question
- In which part of the plants bio-fertilizers are applied?
Correct
Explanation
Bio fertilizers are substances that contain living microorganisms which, when applied to seeds, plant surfaces, or soil, colonize the rhizosphere or the interior of the plant and promote growth by increasing the supply or availability of primary nutrients to the host plant.
Incorrect
Explanation
Bio fertilizers are substances that contain living microorganisms which, when applied to seeds, plant surfaces, or soil, colonize the rhizosphere or the interior of the plant and promote growth by increasing the supply or availability of primary nutrients to the host plant.
-
Question 29 of 135
29. Question
- Which of this bacterium colonizes the roots of leguminous plants?
Correct
Explanation
Rhizobium: Rhizobium is a soil bacterium that colonizes the roots of leguminous plants to form root nodules. The bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert them to ammonia.
Incorrect
Explanation
Rhizobium: Rhizobium is a soil bacterium that colonizes the roots of leguminous plants to form root nodules. The bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert them to ammonia.
-
Question 30 of 135
30. Question
- Which of these crops are inoculated by Azospirillum bacteria?
Correct
Explanation
Azospirillum: Azospirillum bacteria have the ability to use atmospheric nitrogen and transport this nutrient to the crop plants. It is inoculated on maize, barley, oats and sorghum crops. It increases productivity of cereals by 5 -20%, of millets by 30% and fodder by over 50%.
Incorrect
Explanation
Azospirillum: Azospirillum bacteria have the ability to use atmospheric nitrogen and transport this nutrient to the crop plants. It is inoculated on maize, barley, oats and sorghum crops. It increases productivity of cereals by 5 -20%, of millets by 30% and fodder by over 50%.
-
Question 31 of 135
31. Question
- What are the benefits of Azotobacter?
Correct
Explanation
Azotobacter: Application of Azotobacter bacteria has been found to increase yield of wheat, rice, maize and sorghum. Apart from nitrogen fixation, these organisms are capable of producing antifungal and antibacterial compounds.
Incorrect
Explanation
Azotobacter: Application of Azotobacter bacteria has been found to increase yield of wheat, rice, maize and sorghum. Apart from nitrogen fixation, these organisms are capable of producing antifungal and antibacterial compounds.
-
Question 32 of 135
32. Question
- Which of this uptake is increased by Mycorrhizae fungi in vascular plants?
Correct
Explanation
Mycorrhizae: These fungi have symbiotic association with the roots of vascular plants. They increase the uptake of phosphorus. e.g. Citrus, Papaya.
Incorrect
Explanation
Mycorrhizae: These fungi have symbiotic association with the roots of vascular plants. They increase the uptake of phosphorus. e.g. Citrus, Papaya.
-
Question 33 of 135
33. Question
- Assertion (A): Azolla is a free floating aquatic fern having a cyanobacterial association with anabaena.
Reasoning(R): Azolla uses energy from photosynthesis to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Correct
Explanation
Azolla: Azolla is a free floating, aquatic fern found on water surfaces having a cyanobacterial symbiotic association with Anabaena. It is a live floating nitrogen factory using energy from photosynthesis to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Incorrect
Explanation
Azolla: Azolla is a free floating, aquatic fern found on water surfaces having a cyanobacterial symbiotic association with Anabaena. It is a live floating nitrogen factory using energy from photosynthesis to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
-
Question 34 of 135
34. Question
- What is the aim of Biofertiliser scheme of Tamil Nadu government?
Correct
Explanation
Tamil Nadu Government has recently launched ‘Biofertiliser Scheme’. It is aimed at better management of natural farming and helps to boost and maintain soil fertility.
Incorrect
Explanation
Tamil Nadu Government has recently launched ‘Biofertiliser Scheme’. It is aimed at better management of natural farming and helps to boost and maintain soil fertility.
-
Question 35 of 135
35. Question
- Which of these major medicine systems use drugs from plants and animals?
Correct
Explanation
Most medicines are obtained either directly or indirectly from plants. All the major system of medicines such as Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, Homeopathy (AYUSH) use drugs obtained from plants and animals.
Incorrect
Explanation
Most medicines are obtained either directly or indirectly from plants. All the major system of medicines such as Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, Homeopathy (AYUSH) use drugs obtained from plants and animals.
-
Question 36 of 135
36. Question
- Assertion (A): Homeopathy drugs are obtained from plants and animals.
Reasoning(R): The primary metabolites are the drugs obtained from medicinal plants.
Correct
Explanation
Homeopathy use drugs obtained from plants. These drugs from medicinal plants are called secondary metabolites.
Incorrect
Explanation
Homeopathy use drugs obtained from plants. These drugs from medicinal plants are called secondary metabolites.
-
Question 37 of 135
37. Question
- What are the primary metabolites of a plant?
Correct
Explanation
Plants produce primary metabolites for their own living e.g. carbohydrates, amino acids etc.,
Incorrect
Explanation
Plants produce primary metabolites for their own living e.g. carbohydrates, amino acids etc.,
-
Question 38 of 135
38. Question
- What are the functions of secondary metabolites of a plant?
Correct
Explanation
The secondary metabolites for plants are used for protection, competition and species interaction. e.g. alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids etc.
Incorrect
Explanation
The secondary metabolites for plants are used for protection, competition and species interaction. e.g. alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids etc.
-
Question 39 of 135
39. Question
- From which of these the phytochemicals substances are derived?
Correct
Explanation
Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals which are chemical substances derived from various parts of the plant.
Incorrect
Explanation
Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals which are chemical substances derived from various parts of the plant.
-
Question 40 of 135
40. Question
- Which of this botanical name refers to tulsi?
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 41 of 135
41. Question
- Match the drugs with their Tamil names.
Quinine i) Nihya Kalyani
Alkaloids ii) Vetpalai
Terpenoids iii) Cinchona
Flavonoids iv) Nilavembu
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 42 of 135
42. Question
- Which of this drug used as an antidote for snake bite?
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 43 of 135
43. Question
- Which of these plant leaves are not used as a drug?
Correct
Explanation
Drugs derived from Medicinal plants
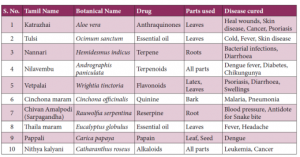 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation
Drugs derived from Medicinal plants

-
Question 44 of 135
44. Question
- Which of these organizations launched the first anti-diabetic drug BGR-34?
Correct
Explanation
The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) and Central Institute for Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP) have jointly launched India’s first anti diabetic ayurvedic drug BGR -34 (BGR-Blood Glucose Regulator). It contains 34 identified active phytoconstituents from herbal resources. It works by controlling blood sugar levels.
Incorrect
Explanation
The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) and Central Institute for Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP) have jointly launched India’s first anti diabetic ayurvedic drug BGR -34 (BGR-Blood Glucose Regulator). It contains 34 identified active phytoconstituents from herbal resources. It works by controlling blood sugar levels.
-
Question 45 of 135
45. Question
- Which of these wastes are used for mushroom cultivation?
Correct
Explanation
Mushroom cultivation is a technology of growing mushrooms using plant, animal and industrial waste. In short it is wealth out of waste technology. This technology has gained importance worldwide because of its dietary fibers and protein value.
Incorrect
Explanation
Mushroom cultivation is a technology of growing mushrooms using plant, animal and industrial waste. In short it is wealth out of waste technology. This technology has gained importance worldwide because of its dietary fibers and protein value.
-
Question 46 of 135
46. Question
- Which type of plant is mushroom?
Correct
Explanation
Mushroom is a fungi belonging to basidiomycetes. It is rich in proteins, fibers, vitamins and minerals.
Incorrect
Explanation
Mushroom is a fungi belonging to basidiomycetes. It is rich in proteins, fibers, vitamins and minerals.
-
Question 47 of 135
47. Question
- Match
Paddy straw mushroom i) Pleurotus species
Oyster mushroom ii) Agaricus bisporus
Button mushroom iii) Volvariella volvacea
Correct
Explanation
There are more than 3000 types of mushrooms. e.g. Button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus), Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus sps.), Paddy straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea).
Incorrect
Explanation
There are more than 3000 types of mushrooms. e.g. Button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus), Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus sps.), Paddy straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea).
-
Question 48 of 135
48. Question
- How many major stages of are involve in mushroom cultivation?
Correct
Explanation
Major stages of mushroom cultivation are Composting, spawning, casing, pinning and harvesting.
Incorrect
Explanation
Major stages of mushroom cultivation are Composting, spawning, casing, pinning and harvesting.
-
Question 49 of 135
49. Question
- How long a composting material is kept at 50°C?
Correct
Explanation
Composting: Compost is prepared by mixing paddy straw with number of organic materials like cow dung and inorganic fertilizers. It is kept at about 50°C for one week.
Incorrect
Explanation
Composting: Compost is prepared by mixing paddy straw with number of organic materials like cow dung and inorganic fertilizers. It is kept at about 50°C for one week.
-
Question 50 of 135
50. Question
- What is spawning?
Correct
Explanation
Spawning: Spawn is the mushroom seed. It is prepared by growing fungal mycelium in grains under sterile conditions. Spawn is sown on compost.
Incorrect
Explanation
Spawning: Spawn is the mushroom seed. It is prepared by growing fungal mycelium in grains under sterile conditions. Spawn is sown on compost.
-
Question 51 of 135
51. Question
- What are the benefits of casing in mushroom cultivation?
Correct
Explanation
Casing: Compost is covered with a thin layer of soil. It gives support to the growing mushroom, provides humidity and helps regulate the temperature.
Incorrect
Explanation
Casing: Compost is covered with a thin layer of soil. It gives support to the growing mushroom, provides humidity and helps regulate the temperature.
-
Question 52 of 135
52. Question
- Which is known as pinning in mushroom harvesting?
Correct
Explanation
Pinning: Mycelium starts to form little bud, which will develop into mushroom. Those little white buds are called pins.
Incorrect
Explanation
Pinning: Mycelium starts to form little bud, which will develop into mushroom. Those little white buds are called pins.
-
Question 53 of 135
53. Question
- Which of the following is not true regarding Mushroom harvesting?
Correct
Explanation
Harvesting: Mushroom grow better in 15°C -23°C. They grow 3 cm in a week which is the normal size for harvesting. In the third week the first flush mushroom can be harvested.
Incorrect
Explanation
Harvesting: Mushroom grow better in 15°C -23°C. They grow 3 cm in a week which is the normal size for harvesting. In the third week the first flush mushroom can be harvested.
-
Question 54 of 135
54. Question
- Which of these are the main problems in mushroom harvesting?
Correct
Explanation
Preservation: Discoloration, weight and flavor loss are the main problems during harvesting of mushrooms.
Incorrect
Explanation
Preservation: Discoloration, weight and flavor loss are the main problems during harvesting of mushrooms.
-
Question 55 of 135
55. Question
- Which of these methods increase the life of mushrooms?
Correct
Explanation
The following methods are used to increase their life. (i) Freezing (ii) Drying (iii) Canning (iv) Vacuum cooling (v) Gamma radiation and storing at 15°C.
Incorrect
Explanation
The following methods are used to increase their life. (i) Freezing (ii) Drying (iii) Canning (iv) Vacuum cooling (v) Gamma radiation and storing at 15°C.
-
Question 56 of 135
56. Question
- By which of this medium hydroponics plants are grown?
Correct
Explanation
Hydroponics is the method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in water. The containers are made of glass, metal or plastic. They range in size from small pots for individual plants to huge tank for large scale growing.
Incorrect
Explanation
Hydroponics is the method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in water. The containers are made of glass, metal or plastic. They range in size from small pots for individual plants to huge tank for large scale growing.
-
Question 57 of 135
57. Question
- Who demonstrated hydroponics method in the year 1980?
Correct
Explanation
Hydroponics was demonstrated by a German Botanist Julius Von Sachs in 1980.
Incorrect
Explanation
Hydroponics was demonstrated by a German Botanist Julius Von Sachs in 1980.
-
Question 58 of 135
58. Question
- In which of this commercial production the hydroponics technique is not used?
Correct
Explanation
Hydroponics is successfully employed for the commercial production of seedless cucumber and tomato. Plants are suspended with their roots submerged in water that contain plant nutrients.
Incorrect
Explanation
Hydroponics is successfully employed for the commercial production of seedless cucumber and tomato. Plants are suspended with their roots submerged in water that contain plant nutrients.
-
Question 59 of 135
59. Question
- Which of this function is externally given to the hydroponics plants?
Correct
Explanation
In Hydroponics the roots absorb water and nutrients, but do not perform the anchoring function. Therefore, the plants must be mechanically supported from above.
Incorrect
Explanation
In Hydroponics the roots absorb water and nutrients, but do not perform the anchoring function. Therefore, the plants must be mechanically supported from above.
-
Question 60 of 135
60. Question
- What is the importance of hydroponics?
Correct
Explanation
Importance of hydroponics
(i) Conservation of water and nutrients.
(ii) Controlled plant growth.
(iii) In deserts and Arctic regions hydroponics can be an effective alternative method.
Incorrect
Explanation
Importance of hydroponics
(i) Conservation of water and nutrients.
(ii) Controlled plant growth.
(iii) In deserts and Arctic regions hydroponics can be an effective alternative method.
-
Question 61 of 135
61. Question
- Choose the correct statements.
- i) The growth medium in aeroponic system is air.
- ii) The roots of aeroponic plants are hanged in the air and misted with water.
iii) The misting of aeroponic plants is done for few weeks.
Correct
Explanation
The aeroponic system is the high-tech type of hydroponic gardening. The growth medium in this type is primarily air. The roots hang in the air and are misted with nutrient solution. The misting is usually done for every few minutes, as roots will dry out rapidly if the misting cycles are interrupted.
Incorrect
Explanation
The aeroponic system is the high-tech type of hydroponic gardening. The growth medium in this type is primarily air. The roots hang in the air and are misted with nutrient solution. The misting is usually done for every few minutes, as roots will dry out rapidly if the misting cycles are interrupted.
-
Question 62 of 135
62. Question
- What is the significance of aeroponic technique?
Correct
Explanation
In aeroponic plants a timer controls the nutrient pump much like other types of hydroponic systems except that the aeroponic system needs a short cycle timer that runs the pump for a few seconds every couple of minutes.
Incorrect
Explanation
In aeroponic plants a timer controls the nutrient pump much like other types of hydroponic systems except that the aeroponic system needs a short cycle timer that runs the pump for a few seconds every couple of minutes.
-
Question 63 of 135
63. Question
- Which of this combination provides the aquaponics system?
Correct
Explanation
Aquaponics is a system of a combination of conventional aquaculture with hydroponics in a symbiotic environment, in which plants are fed with the aquatic animals’ excreta or wastes.
Incorrect
Explanation
Aquaponics is a system of a combination of conventional aquaculture with hydroponics in a symbiotic environment, in which plants are fed with the aquatic animals’ excreta or wastes.
-
Question 64 of 135
64. Question
- What type of nutrient is utilized by the aquaponics plants?
Correct
Explanation
The animal wastes are broken down by nitrifying bacteria initially into nitrites and later into nitrates that are utilized by the plants as their nutrients. Thus the wastes are utilized and water is re-circulated back to the aquaculture system.
Incorrect
Explanation
The animal wastes are broken down by nitrifying bacteria initially into nitrites and later into nitrates that are utilized by the plants as their nutrients. Thus the wastes are utilized and water is re-circulated back to the aquaculture system.
-
Question 65 of 135
65. Question
- Which of this technique is used for raising plants in aquaponics?
Correct
Explanation
Aquaponics consists of two main parts, aquaculture- for raising aquatic animals like fish and hydroponics-for raising plants.
Incorrect
Explanation
Aquaponics consists of two main parts, aquaculture- for raising aquatic animals like fish and hydroponics-for raising plants.
-
Question 66 of 135
66. Question
- Which of these plants cannot be grown in aquaponics?
Correct
Explanation
Green leafy vegetables like Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, coriander, parsley, spinach and vegetables like tomatoes, capsicum, chilies, bell peppers, sweet potato, cauliflower, broccoli and egg-plant can be grown in aquaponics.
Incorrect
Explanation
Green leafy vegetables like Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, coriander, parsley, spinach and vegetables like tomatoes, capsicum, chilies, bell peppers, sweet potato, cauliflower, broccoli and egg-plant can be grown in aquaponics.
-
Question 67 of 135
67. Question
- Assertion (A): Dairying is the production and marketing of milk and its products.
Reasoning(R): Cattle rising, collection and processing of milk and milk products are involved in dairying.
Correct
Explanation
Dairy farming involves rising of cattle for milk production. It involves the proper maintenance of cattle, along with collection and processing of milk and milk products which are useful to man. Dairying is the production and marketing of milk and its products.
Incorrect
Explanation
Dairy farming involves rising of cattle for milk production. It involves the proper maintenance of cattle, along with collection and processing of milk and milk products which are useful to man. Dairying is the production and marketing of milk and its products.
-
Question 68 of 135
68. Question
- Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The Indian cattle include cows and buffaloes.
ii) Indian cattle’s belongs to five different species.
iii) Cattles are domesticated for milk, meat and leather transportation.
Correct
Explanation
The Indian cattle include cows and buffaloes. They are domesticated for milk, meat, leather and transportation. They belong to two different species, Bos indicus (Indian cows and bulls) and Bos bubalis (buffaloes).
Incorrect
Explanation
The Indian cattle include cows and buffaloes. They are domesticated for milk, meat, leather and transportation. They belong to two different species, Bos indicus (Indian cows and bulls) and Bos bubalis (buffaloes).
-
Question 69 of 135
69. Question
- How many breeds are classified in Indian cattle animals?
Correct
Explanation
The Indian cattle animals are reared for milk and farm labor. They are classified into three types: Dairy breeds, Draught (or) Draft breeds, Dual purpose breeds.
Incorrect
Explanation
The Indian cattle animals are reared for milk and farm labor. They are classified into three types: Dairy breeds, Draught (or) Draft breeds, Dual purpose breeds.
-
Question 70 of 135
70. Question
- What are the dairy breeds available for domestication?
Correct
Explanation
Dairy breeds: Dairy animals are domesticated for obtaining milk. The cows (milk producing females) are high milk yielders (milch animals). The dairy breeds are: Indigenous breeds, Exotic breeds.
Incorrect
Explanation
Dairy breeds: Dairy animals are domesticated for obtaining milk. The cows (milk producing females) are high milk yielders (milch animals). The dairy breeds are: Indigenous breeds, Exotic breeds.
-
Question 71 of 135
71. Question
- Which of these statements are not true regarding the Indigenous breeds of India?
Correct
Explanation
Indigenous breeds are native of India. They include Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, Deoni and Gir. These cattle are well built with strong limbs, prominent hump and loose skin. Milk production depends on the duration of the lactation period (the period of milk production after the birth of a calf). These local breed animals show excellent resistant to diseases.
Incorrect
Explanation
Indigenous breeds are native of India. They include Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, Deoni and Gir. These cattle are well built with strong limbs, prominent hump and loose skin. Milk production depends on the duration of the lactation period (the period of milk production after the birth of a calf). These local breed animals show excellent resistant to diseases.
-
Question 72 of 135
72. Question
- On what basis the exotic breeds are selected from foreign countries?
Correct
Explanation
Exotic breeds (Bos Taurus) are imported from foreign countries. They include Jersey, Brown Swiss and Holstein-Friesian etc. These foreign breeds are selected for long lactation periods.
Incorrect
Explanation
Exotic breeds (Bos Taurus) are imported from foreign countries. They include Jersey, Brown Swiss and Holstein-Friesian etc. These foreign breeds are selected for long lactation periods.
-
Question 73 of 135
73. Question
- Which of this is not a draught breed of India?
Correct
Explanation
Draught (or) Draft breeds: They are used for agricultural work, such as tilling, irrigation and carting. These include Amritmahal, Kangayam, Umblachery, Malvi, Siri and Hallikar breeds. Bullocks are good draft animals while the cows are poor milk yielders.
Incorrect
Explanation
Draught (or) Draft breeds: They are used for agricultural work, such as tilling, irrigation and carting. These include Amritmahal, Kangayam, Umblachery, Malvi, Siri and Hallikar breeds. Bullocks are good draft animals while the cows are poor milk yielders.
-
Question 74 of 135
74. Question
- Which of these belongs to the Dual purpose breeds in India?
Correct
Explanation
Dual purpose breeds: The cows of these breeds provide milk and the bulls are useful for farm work. In India these breeds are favored by farmers. They include Haryana, Ongole, Kankrej and Tharparkar.
Incorrect
Explanation
Dual purpose breeds: The cows of these breeds provide milk and the bulls are useful for farm work. In India these breeds are favored by farmers. They include Haryana, Ongole, Kankrej and Tharparkar.
-
Question 75 of 135
75. Question
- Which of these breed belongs to Tamil Nadu?
Correct
Explanation
Indigenous Draught breeds – Native to Tamil Nadu
Kangayam: It originated in Kangayam and is observed in Dharapuram, Perundurai, Erode, Bhavani and part of Gobichettipalayam Taluk of Erode and Coimbatore district.
Pulikulam: This breed is commonly seen in Cumbum valley of Madurai district in Tamil Nadu. It is also known as Jallikattu madu. They are mainly used for penning in the field and useful for ploughing.
Incorrect
Explanation
Indigenous Draught breeds – Native to Tamil Nadu
Kangayam: It originated in Kangayam and is observed in Dharapuram, Perundurai, Erode, Bhavani and part of Gobichettipalayam Taluk of Erode and Coimbatore district.
Pulikulam: This breed is commonly seen in Cumbum valley of Madurai district in Tamil Nadu. It is also known as Jallikattu madu. They are mainly used for penning in the field and useful for ploughing.
-
Question 76 of 135
76. Question
- How many types are feeds are classified for dairy cattle’s?
Correct
Explanation
The food requirement for cattle should support healthy life of the animal and milk producing requirement. The feed for dairy cattle is broadly classified into two: Roughages and Concentrates.
Incorrect
Explanation
The food requirement for cattle should support healthy life of the animal and milk producing requirement. The feed for dairy cattle is broadly classified into two: Roughages and Concentrates.
-
Question 77 of 135
77. Question
- Which of these included in the roughage feeds?
Correct
Explanation
Roughage is a coarse and fibrous fodder. It consists of succulent feed (cultivated grass, fodder and root crops) and dry fodder (hay, straw and chaff).
Incorrect
Explanation
Roughage is a coarse and fibrous fodder. It consists of succulent feed (cultivated grass, fodder and root crops) and dry fodder (hay, straw and chaff).
-
Question 78 of 135
78. Question
- Which of these statements are true regarding Concentrates?
i) Concentrates are high in fiber and contain carbohydrates, protein and other nutrients.
ii) Rice bran, wheat bran, mango seed, Neem cake and sesame cake can be used to make concentrate feeds.
iii) Green fodder is not included in concentrate feeds.
Correct
Explanation
Concentrates are low in fiber and contain high level of carbohydrates, protein and other nutrients. A variety of raw materials such as Cholam (Jowar), kambu (pearl millet), ragi (finger millet), rice bran, wheat bran, cotton seed cake, mustard cake, linseed cake, groundnut cake, mango seed, neem cake and yellu (sesame) cake can be used to make concentrate feed. They should also be fed on green fodder (maize, lucerne, berseem, and millet and elephant grass).
Incorrect
Explanation
Concentrates are low in fiber and contain high level of carbohydrates, protein and other nutrients. A variety of raw materials such as Cholam (Jowar), kambu (pearl millet), ragi (finger millet), rice bran, wheat bran, cotton seed cake, mustard cake, linseed cake, groundnut cake, mango seed, neem cake and yellu (sesame) cake can be used to make concentrate feed. They should also be fed on green fodder (maize, lucerne, berseem, and millet and elephant grass).
-
Question 79 of 135
79. Question
- Which of these food additives promote the growth of animals and yield?
Correct
Explanation
Dairy cattle need balanced rations containing all nutrients in proportional amounts and food additives which contain minerals, vitamins, antibiotics and hormones to promote the growth of animals, good yield of milk and to protect them from diseases.
Incorrect
Explanation
Dairy cattle need balanced rations containing all nutrients in proportional amounts and food additives which contain minerals, vitamins, antibiotics and hormones to promote the growth of animals, good yield of milk and to protect them from diseases.
-
Question 80 of 135
80. Question
- Which of these is not included in a daily average feed of a milking cow?
Correct
Explanation
The daily average feed ratio of a milking cow is: 15-25 kg of roughage (dry grass and green fodder), 4-5 kg of grain mixture, 100-150 liters of water.
Incorrect
Explanation
The daily average feed ratio of a milking cow is: 15-25 kg of roughage (dry grass and green fodder), 4-5 kg of grain mixture, 100-150 liters of water.
-
Question 81 of 135
81. Question
- Who was the architect of India’s Modern Dairy Industry?
Correct
Explanation
Dr. Verghese Kurein was the founder of National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and was called the Architect of India’s Modern Dairy Industry and the Father of White Revolution.
Incorrect
Explanation
Dr. Verghese Kurein was the founder of National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and was called the Architect of India’s Modern Dairy Industry and the Father of White Revolution.
-
Question 82 of 135
82. Question
- When did White Revolution started in India?
Correct
Explanation
Operation Flood or the White revolution started in the year 1970 and was aimed to create a nationwide milk grid. It was a rural development program initiated by NDDB – National Dairy Development Board of India
Incorrect
Explanation
Operation Flood or the White revolution started in the year 1970 and was aimed to create a nationwide milk grid. It was a rural development program initiated by NDDB – National Dairy Development Board of India
-
Question 83 of 135
83. Question
- Which of the following is the largest dairy development program of NDDB, India?
Correct
Explanation
NDDB designed and implemented the world’s largest dairy development program called OPERATION FLOOD. Operation Flood Program is based on dairy commodity aid to increase milk supply in urban areas.
Incorrect
Explanation
NDDB designed and implemented the world’s largest dairy development program called OPERATION FLOOD. Operation Flood Program is based on dairy commodity aid to increase milk supply in urban areas.
-
Question 84 of 135
84. Question
- Which of these are included in the Intensive Cattle development program?
Correct
Explanation
Intensive Cattle Development Program: It is based on cross breeding of indigenous cows with exotic (European) breeds to increase milk production. New methods and modern equipment’s are made available for machine –milking of cows.
Incorrect
Explanation
Intensive Cattle Development Program: It is based on cross breeding of indigenous cows with exotic (European) breeds to increase milk production. New methods and modern equipment’s are made available for machine –milking of cows.
-
Question 85 of 135
85. Question
- What is the significance of aquaculture?
Correct
Explanation
Aquaculture is the rearing of economically important aquatic organisms like fishes, prawns, shrimps, crabs, lobsters, edible oysters, pearl oysters and seaweeds under controlled and confined environmental conditions using advanced technologies.
Incorrect
Explanation
Aquaculture is the rearing of economically important aquatic organisms like fishes, prawns, shrimps, crabs, lobsters, edible oysters, pearl oysters and seaweeds under controlled and confined environmental conditions using advanced technologies.
-
Question 86 of 135
86. Question
- How many types of aquaculture are classified?
Correct
Explanation
Aquaculture is classified into: Freshwater aquaculture, Marine water aquaculture (Mariculture)
Incorrect
Explanation
Aquaculture is classified into: Freshwater aquaculture, Marine water aquaculture (Mariculture)
-
Question 87 of 135
87. Question
- Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Freshwater aquaculture involves rearing of aquatic organisms in freshwater.
ii) Culture of organism is carried in pond, river, dam and cold water.
iii) Freshwater resources remain in land and sea water.
Correct
Explanation
Freshwater aquaculture: The rearing of aquatic organisms in freshwater is called freshwater aquaculture. Culture of organisms is carried out in pond, river, dam, lake and cold water. These freshwater resources remain within the land.
Incorrect
Explanation
Freshwater aquaculture: The rearing of aquatic organisms in freshwater is called freshwater aquaculture. Culture of organisms is carried out in pond, river, dam, lake and cold water. These freshwater resources remain within the land.
-
Question 88 of 135
88. Question
- Which of these fishes are not cultured in freshwater?
Correct
Explanation
Tilapia, carps (Catla, Rohu, and Mrigal), catfishes and air breathing fishes are cultured in freshwater.
Incorrect
Explanation
Tilapia, carps (Catla, Rohu, and Mrigal), catfishes and air breathing fishes are cultured in freshwater.
-
Question 89 of 135
89. Question
- What type of aquaculture is followed in Tamil Nadu?
Correct
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is a leading state endowed with rich fishery resources from Marine, Inland and Coastal Aquaculture. The marine fisheries potential of the state is estimated at 0.719 million tonnes. The inland fishery resources have a potential to yield 4.5 lakh metric tonnes of fishes.
Incorrect
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is a leading state endowed with rich fishery resources from Marine, Inland and Coastal Aquaculture. The marine fisheries potential of the state is estimated at 0.719 million tonnes. The inland fishery resources have a potential to yield 4.5 lakh metric tonnes of fishes.
-
Question 90 of 135
90. Question
- What is the national rank of Tamil Nadu in coastal farming?
Correct
Explanation
Tamilnadu ranks sixth among the maritime states in coastal farming.
Incorrect
Explanation
Tamilnadu ranks sixth among the maritime states in coastal farming.
-
Question 91 of 135
91. Question
- Which of these methods cultivate aquatic organisms in sea water?
Correct
Explanation
Marine water aquaculture: The cultivation of aquatic organisms is in sea water. This is also referred as Mariculture or Sea farming.
Incorrect
Explanation
Marine water aquaculture: The cultivation of aquatic organisms is in sea water. This is also referred as Mariculture or Sea farming.
-
Question 92 of 135
92. Question
Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Culture of organisms is carried out along the sea coast only.
ii) Salmons, sea bass, milk fishes and mullets are cultured in marine water.
Correct
Explanation
Culture of organisms is carried out along the sea coast (inshore area) and in deep sea. Organisms like shrimps (marine prawns), pearl oysters, edible oysters, mussels and fin fishes like salmons, sea bass, milk fishes and mullets are cultured in marine water.
Incorrect
Explanation
Culture of organisms is carried out along the sea coast (inshore area) and in deep sea. Organisms like shrimps (marine prawns), pearl oysters, edible oysters, mussels and fin fishes like salmons, sea bass, milk fishes and mullets are cultured in marine water.
-
Question 93 of 135
93. Question
- Which of this revolution is related with aquaculture?
Correct
Explanation
Aquaculture aims at blue revolution. It is a major source of export and foreign exchange earnings for the country. It generates employment through fish farming in rural and under developed area.
Incorrect
Explanation
Aquaculture aims at blue revolution. It is a major source of export and foreign exchange earnings for the country. It generates employment through fish farming in rural and under developed area.
-
Question 94 of 135
94. Question
- Assertion (A): Pisciculture is the process of breeding and rearing of fishes in reservoirs, lakes and paddy fields.
Reasoning(R): The Economically important fishes are farmed under controlled conditions in pisciculture.
Correct
Explanation
Pisciculture or Fish culture is the process of breeding and rearing of fishes in ponds, reservoirs (dams), lakes, rivers and paddy fields. It is the farming of economically important fishes under controlled conditions.
Incorrect
Explanation
Pisciculture or Fish culture is the process of breeding and rearing of fishes in ponds, reservoirs (dams), lakes, rivers and paddy fields. It is the farming of economically important fishes under controlled conditions.
-
Question 95 of 135
95. Question
- Match
Polyculture i) Low stocking density
Intensive fish culture ii) Mono species culture
Monoculture iii) Composite fish culture
Extensive fish culture iv) Artificial feeding
Correct
Explanation
Extensive fish culture: Culture of fishes in large areas with low stocking density and natural feeding. Intensive fish culture: Culture of fishes in small areas with high stocking density and providing artificial feed to increase production. Monoculture: It is the culture of single type of fish in a water body. It is also called mono species culture. Polyculture: It is the culture of more than one type of fish in a water body. It is also called composite fish culture. Integrated fish farming: It is the culture of fishes along with agricultural crops or animal husbandry farming. Rearing of fish along with paddy, poultry, cattle, pig and ducks.
Incorrect
Explanation
Extensive fish culture: Culture of fishes in large areas with low stocking density and natural feeding. Intensive fish culture: Culture of fishes in small areas with high stocking density and providing artificial feed to increase production. Monoculture: It is the culture of single type of fish in a water body. It is also called mono species culture. Polyculture: It is the culture of more than one type of fish in a water body. It is also called composite fish culture. Integrated fish farming: It is the culture of fishes along with agricultural crops or animal husbandry farming. Rearing of fish along with paddy, poultry, cattle, pig and ducks.
-
Question 96 of 135
96. Question
- Assertion (A): The Mature male and female fishes are collected in the breeding pond.
Reasoning(R): The fertilized eggs are transferred into hatching pits for hatching.
Correct
Explanation
Fish farm requires different types of pond for the various developmental stages of fish growth.
Breeding pond: Healthy and sexually mature male and female fishes are collected and introduced in this pond for breeding. The eggs released by the female are fertilized by the sperm and fertilized eggs float in water as frothy mass.
Hatching pits: The fertilized eggs are transferred to hatching pits or hatching hapas for hatching.
Incorrect
Explanation
Fish farm requires different types of pond for the various developmental stages of fish growth.
Breeding pond: Healthy and sexually mature male and female fishes are collected and introduced in this pond for breeding. The eggs released by the female are fertilized by the sperm and fertilized eggs float in water as frothy mass.
Hatching pits: The fertilized eggs are transferred to hatching pits or hatching hapas for hatching.
-
Question 97 of 135
97. Question
- What is the maximum length of the fry in a nursery pond?
Correct
Explanation
Nursery ponds: The hatchlings are transferred from hatching pits after 2 to 7 days. The hatchlings grow into fry and are cultured in these ponds for about 60 days with proper feeding till they reach 2 – 2.5 cm in length.
Incorrect
Explanation
Nursery ponds: The hatchlings are transferred from hatching pits after 2 to 7 days. The hatchlings grow into fry and are cultured in these ponds for about 60 days with proper feeding till they reach 2 – 2.5 cm in length.
-
Question 98 of 135
98. Question
- Choose the Incorrect statements regarding rearing ponds.
i) The fish fry is developed as fingerlings in the rearing ponds.
ii) In the rearing ponds the fish fry reaches 10 to 15 cm length.
iii) The fish fry are transferred to nursery ponds from the rearing ponds.
Correct
Explanation
Rearing ponds: Rearing ponds are used to culture the fry. The fish fry are transferred from nursery pond to rearing ponds and are maintained for about three months till they reach 10 to 15 cm in length. In these rearing ponds the fry develops into fingerlings.
Incorrect
Explanation
Rearing ponds: Rearing ponds are used to culture the fry. The fish fry are transferred from nursery pond to rearing ponds and are maintained for about three months till they reach 10 to 15 cm in length. In these rearing ponds the fry develops into fingerlings.
-
Question 99 of 135
99. Question
- What are the other names for stocking pond?
Correct
Explanation
Stocking pond: The stocking pond is also called as culture pond or production pond. These ponds are used to rear fingerlings up to the marketable size.
Incorrect
Explanation
Stocking pond: The stocking pond is also called as culture pond or production pond. These ponds are used to rear fingerlings up to the marketable size.
-
Question 100 of 135
100. Question
- Which of these fishes are freshwater cultivable?
Correct
Explanation
Freshwater cultivable fishes: Indian major carps (Kendai) – Catla, Rohu, Mrigal, catfishes (Keluthi), Murrels (Veral) and Tilapia (Jilebi kendai) are cultured in freshwater.
Incorrect
Explanation
Freshwater cultivable fishes: Indian major carps (Kendai) – Catla, Rohu, Mrigal, catfishes (Keluthi), Murrels (Veral) and Tilapia (Jilebi kendai) are cultured in freshwater.
-
Question 101 of 135
101. Question
- Which of these does not belong to the marine water cultivable fishes?
Correct
Explanation
Marine water cultivable fishes: Sea bass (Koduva), Grey mullet (Madavai) and Chanos chanos (Milk fish) are the fishes cultured in marine water.
Incorrect
Explanation
Marine water cultivable fishes: Sea bass (Koduva), Grey mullet (Madavai) and Chanos chanos (Milk fish) are the fishes cultured in marine water.
-
Question 102 of 135
102. Question
- Which of the following is not a water soluble vitamin?
Correct
Explanation
Fat soluble vitamins A, D and water soluble B-complex vitamins like pyridoxine, cyanocobalamine and niacin.
Incorrect
Explanation
Fat soluble vitamins A, D and water soluble B-complex vitamins like pyridoxine, cyanocobalamine and niacin.
-
Question 103 of 135
103. Question
- Which are the most economically important fish resources in India?
Correct
Explanation
One of the most economically important shell fish resources of India are prawns. They are of great demand both in the local and international market. Due to their great taste, they are a cherished delicacy to be served as food. In view of their popularity and marketing avenues in foreign countries there is a need for developing advanced technology and intensify prawn culture in India.
Incorrect
Explanation
One of the most economically important shell fish resources of India are prawns. They are of great demand both in the local and international market. Due to their great taste, they are a cherished delicacy to be served as food. In view of their popularity and marketing avenues in foreign countries there is a need for developing advanced technology and intensify prawn culture in India.
-
Question 104 of 135
104. Question
- What are the factors considered for commercial prawn culture?
Correct
Explanation
A number of species of prawns of different sizes are found distributed in water resources. Only those prawns which are good in size, weight, available in plenty and easily cultivable are commonly selected for prawn culture on commercial basis.
Incorrect
Explanation
A number of species of prawns of different sizes are found distributed in water resources. Only those prawns which are good in size, weight, available in plenty and easily cultivable are commonly selected for prawn culture on commercial basis.
-
Question 105 of 135
105. Question
- Which of these prawns are reared in marine water prawn culture?
Correct
Explanation
Marine water prawn culture: The rearing of marine penaied prawn is called marine prawn culture or shrimp culture. Penaeus indicus and Penaeus monodon are cultured in marine water.
Incorrect
Explanation
Marine water prawn culture: The rearing of marine penaied prawn is called marine prawn culture or shrimp culture. Penaeus indicus and Penaeus monodon are cultured in marine water.
-
Question 106 of 135
106. Question
- Assertion (A): Rearing of freshwater prawn is called as Freshwater prawn culture.
Reasoning(R): Macrobrachium rosenbergii is a fresh water prawn.
Correct
Explanation
The rearing of freshwater prawn is called freshwater prawn culture. Macrobrachium rosenbergii and Macrobrachium malcomsonii are cultured in freshwater.
Incorrect
Explanation
The rearing of freshwater prawn is called freshwater prawn culture. Macrobrachium rosenbergii and Macrobrachium malcomsonii are cultured in freshwater.
-
Question 107 of 135
107. Question
- Which of these methods is not employed for prawn culture?
Correct
Explanation
The methods employed for prawn culture are: Seed collection and hatchery method, Paddy cum prawn culture method.
Incorrect
Explanation
The methods employed for prawn culture are: Seed collection and hatchery method, Paddy cum prawn culture method.
-
Question 108 of 135
108. Question
- By which of these methods seed collection and hatchery techniques are executed?
Correct
Explanation
Seed collection and hatchery method: The larvae and juveniles obtained by collection from natural resources (estuaries, and backwaters) or by hatchery methods (controlled breeding). They are reared and grown into adults.
Incorrect
Explanation
Seed collection and hatchery method: The larvae and juveniles obtained by collection from natural resources (estuaries, and backwaters) or by hatchery methods (controlled breeding). They are reared and grown into adults.
-
Question 109 of 135
109. Question
- Which part of India practices the Pokkali culture?
Correct
Explanation
Paddy cum prawn culture: It is also called Pokkali culture. It is the oldest and traditional method of prawn culture practiced in Kerala. The low lying paddy fields along the coastal areas serve as suitable grounds for prawn culture. Prawns are cultured in these fields after the harvest of paddy.
Incorrect
Explanation
Paddy cum prawn culture: It is also called Pokkali culture. It is the oldest and traditional method of prawn culture practiced in Kerala. The low lying paddy fields along the coastal areas serve as suitable grounds for prawn culture. Prawns are cultured in these fields after the harvest of paddy.
-
Question 110 of 135
110. Question
- State the technology used to maintain organic matter of the soil and productivity.
Correct
Explanation
The awareness of organic matter and concept of sustainable agriculture is gaining importance among our farmers in the recent years to produce good quality crops. Maintenance of soil organic matter is very important for sustainable productivity and this is attained by Vermitechnology.
Incorrect
Explanation
The awareness of organic matter and concept of sustainable agriculture is gaining importance among our farmers in the recent years to produce good quality crops. Maintenance of soil organic matter is very important for sustainable productivity and this is attained by Vermitechnology.
-
Question 111 of 135
111. Question
- Assertion (A): Vermiculture refers to artificial rearing or cultivation of earthworms.
Reasoning(R): It is used to produce compost from natural organic wastes.
Correct
Explanation
Vermiculture involves the artificial rearing or cultivation of earthworms and using them for the production of compost from natural organic wastes.
Incorrect
Explanation
Vermiculture involves the artificial rearing or cultivation of earthworms and using them for the production of compost from natural organic wastes.
-
Question 112 of 135
112. Question
- Match
Red worm i) Eudrilus eugeniae
Indian Blue worm ii) Perionyx excavatus
African Night crawler iii) Eisenia fetida
Correct
Explanation
The earthworms used for vermicomposting production are Perionyx excavatus (Indian blue worm), Eisenia fetida (Red worms), and Eudrilus eugeniae (African night crawler).
Incorrect
Explanation
The earthworms used for vermicomposting production are Perionyx excavatus (Indian blue worm), Eisenia fetida (Red worms), and Eudrilus eugeniae (African night crawler).
-
Question 113 of 135
113. Question
- Choose the correct statements.
i) Vermicomposting method converts bio-wastes into nutrient organic manure by earthworms.
ii) The organic wastes are excreted by the earthworms known as castings.
Correct
Explanation
Vermicomposting: It is an important component of organic farming which can convert bio-wastes into nutrient rich organic manure by using earthworms. It feeds on the organic wastes and excretes it in digested form known as castings. The compost is generally called vermicompost.
Incorrect
Explanation
Vermicomposting: It is an important component of organic farming which can convert bio-wastes into nutrient rich organic manure by using earthworms. It feeds on the organic wastes and excretes it in digested form known as castings. The compost is generally called vermicompost.
-
Question 114 of 135
114. Question
- Assertion (A): Vermicompost is an ideal fertilizer for increasing the nutrients of the soil.
Reasoning(R): Vermicompost is formed by decomposing organic materials by the earthworm.
Correct
Explanation
Vermicompost is the excreta (worm castings) which is a fine, granular organic matter formed by the decomposition of organic materials by the earthworm. It is an ideal fertilizer for the soil.
Incorrect
Explanation
Vermicompost is the excreta (worm castings) which is a fine, granular organic matter formed by the decomposition of organic materials by the earthworm. It is an ideal fertilizer for the soil.
-
Question 115 of 135
115. Question
- What are the organic sources for vermicomposting?
Correct
Explanation
Biologically degradable organic wastes are used as potential organic resources for vermicomposting. They are:
- Agricultural wastes (crop residue, vegetables waste, sugarcane trash)
- Crop residues (rice straw, tea wastes, cereal and pulse residues, rice husk, tobacco wastes, coir wastes)
- Leaf litter
- Fruit and vegetable wastes
- Animal wastes (cattle dung, poultry droppings, pig slurry, goat and sheep droppings)
- Biogas slurry
Incorrect
Explanation
Biologically degradable organic wastes are used as potential organic resources for vermicomposting. They are:
- Agricultural wastes (crop residue, vegetables waste, sugarcane trash)
- Crop residues (rice straw, tea wastes, cereal and pulse residues, rice husk, tobacco wastes, coir wastes)
- Leaf litter
- Fruit and vegetable wastes
- Animal wastes (cattle dung, poultry droppings, pig slurry, goat and sheep droppings)
- Biogas slurry
-
Question 116 of 135
116. Question
- What is the bedding materials filled in a vermicomposting bin method?
Correct
Explanation
Vermicomposting by Bin Method: It is the rearing of earthworms in a container or bin. The container is half filled with bedding materials such as shredded cardboard, leaves, paddy husk, chopped straw, saw dust and manure. Small quantity of soil and sand is added to provide necessary grit for the worms. The bedding material should be moistened by adding water that enables free movements of the worms. The worms are gently placed and spread evenly on the bedding.
Incorrect
Explanation
Vermicomposting by Bin Method: It is the rearing of earthworms in a container or bin. The container is half filled with bedding materials such as shredded cardboard, leaves, paddy husk, chopped straw, saw dust and manure. Small quantity of soil and sand is added to provide necessary grit for the worms. The bedding material should be moistened by adding water that enables free movements of the worms. The worms are gently placed and spread evenly on the bedding.
-
Question 117 of 135
117. Question
- After how many days the organic wastes are transformed to nutrient materials in vermicomposting bin method?
Correct
Explanation
Organic wastes (kitchen wastes, vegetable and fruit wastes) are added which are fed by the earthworms. The bin is covered with coconut leaves or gunny bags to conserve moisture provide darkness and keep out of pests. After a period of 60 days the wastes are completely transformed into nutrient rich materials that are excreted by earthworms known as worm castings.
Incorrect
Explanation
Organic wastes (kitchen wastes, vegetable and fruit wastes) are added which are fed by the earthworms. The bin is covered with coconut leaves or gunny bags to conserve moisture provide darkness and keep out of pests. After a period of 60 days the wastes are completely transformed into nutrient rich materials that are excreted by earthworms known as worm castings.
-
Question 118 of 135
118. Question
- Which of these statements is not true regarding Vermicompost?
Correct
Explanation
Vermicompost is dark brown in color and similar to farmyard manure in color and appearance.
- It is a rich source of nutrients essential for plant growth. It makes the soil fertile.
- It improves the water holding capacity and helps to prevent soil erosion.
- It contains valuable vitamins, enzymes and growth regulator substances for increasing growth, vigour and yield of plants.
- It enhances decomposition of organic matter in soil.
- Vermicompost is free from pathogens and toxic elements.
- Vermicompost is rich in beneficial microflora.
Incorrect
Explanation
Vermicompost is dark brown in color and similar to farmyard manure in color and appearance.
- It is a rich source of nutrients essential for plant growth. It makes the soil fertile.
- It improves the water holding capacity and helps to prevent soil erosion.
- It contains valuable vitamins, enzymes and growth regulator substances for increasing growth, vigour and yield of plants.
- It enhances decomposition of organic matter in soil.
- Vermicompost is free from pathogens and toxic elements.
- Vermicompost is rich in beneficial microflora.
-
Question 119 of 135
119. Question
- Which of these refers to Bee keeping?
Correct
Explanation
Apiculture is the rearing of honey bee for honey. It is also called Bee keeping. It is a profitable rural based industry. Honey bees are domesticated by farmers to produce honey.
Incorrect
Explanation
Apiculture is the rearing of honey bee for honey. It is also called Bee keeping. It is a profitable rural based industry. Honey bees are domesticated by farmers to produce honey.
-
Question 120 of 135
120. Question
- How many types of bee are available in a honey bee colony?
Correct
Explanation
There are three types of individuals in a honey bee colony namely the queen bee, the drones and the worker bees.
Incorrect
Explanation
There are three types of individuals in a honey bee colony namely the queen bee, the drones and the worker bees.
-
Question 121 of 135
121. Question
- Which of these statements are true regarding Queen Bee?
Correct
Explanation
Queen Bee: The queen is the largest member and the fertile female of the colony. They are formed from fertile eggs. The queen is responsible for laying eggs in a colony.
Incorrect
Explanation
Queen Bee: The queen is the largest member and the fertile female of the colony. They are formed from fertile eggs. The queen is responsible for laying eggs in a colony.
-
Question 122 of 135
122. Question
- Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the drones.
i) Fertile males are developed from unfertilized eggs.
ii) Larger than the Queen and the worker bees.
iii) The main function is to fertilize the eggs produced by the queen.
Correct
Explanation
Drones: They are the fertile males. They develop from unfertilized eggs. They are larger than the workers and smaller than the queens. Their main function is to fertilize the eggs produced by the queen.
Incorrect
Explanation
Drones: They are the fertile males. They develop from unfertilized eggs. They are larger than the workers and smaller than the queens. Their main function is to fertilize the eggs produced by the queen.
-
Question 123 of 135
123. Question
- What are the functions of worker bees?
Correct
Explanation
Worker Bees: They are sterile female bees and are the smallest members of the colony. Their function is to collect honey, look after the young ones, clean the comb, defend the hive and maintain the temperature of the bee hive.
Incorrect
Explanation
Worker Bees: They are sterile female bees and are the smallest members of the colony. Their function is to collect honey, look after the young ones, clean the comb, defend the hive and maintain the temperature of the bee hive.
-
Question 124 of 135
124. Question
- Which is not an indigenous variety honey bee?
Correct
Explanation
Varieties of Honey Bee
Indigenous varieties
i) Apis dorsata (Rock bee or Wild bee)
ii) Apis florea (Little bee)
iii) Apis indica (Indian bee)
Incorrect
Explanation
Varieties of Honey Bee
Indigenous varieties
i) Apis dorsata (Rock bee or Wild bee)
ii) Apis florea (Little bee)
iii) Apis indica (Indian bee)
-
Question 125 of 135
125. Question
- Which of the following is an African species of honey bee?
Correct
Explanation
Exotic varieties
i) Apis mellifera (Italian bee)
ii) Apis adamsoni (African bee)
Incorrect
Explanation
Exotic varieties
i) Apis mellifera (Italian bee)
ii) Apis adamsoni (African bee)
-
Question 126 of 135
126. Question
- Assertion (A): A Honey comb is a vertical sheet of wax with double layer of hexagonal cells.
Reasoning(R): The comb of the bee hive is formed by the wax glands of the worker bees.
Correct
Explanation
The comb of the bees is formed mainly by the secretion of the wax glands present in the abdomen of the worker bee. A comb is a vertical sheet of wax with double layer of hexagonal cells.
Incorrect
Explanation
The comb of the bees is formed mainly by the secretion of the wax glands present in the abdomen of the worker bee. A comb is a vertical sheet of wax with double layer of hexagonal cells.
-
Question 127 of 135
127. Question
- In which part of the bee hive the nectar is converted into honey?
Correct
Explanation
Formation of Honey: The honey bees suck the nectar from various flowers. The nectar passes to the honey sac. In the honey sac, sucrose present in the nectar mixes with acidic secretion and by enzymatic action it is converted into honey which is stored in the special chambers of the hive.
Incorrect
Explanation
Formation of Honey: The honey bees suck the nectar from various flowers. The nectar passes to the honey sac. In the honey sac, sucrose present in the nectar mixes with acidic secretion and by enzymatic action it is converted into honey which is stored in the special chambers of the hive.
-
Question 128 of 135
128. Question
- Which of this factor decides the quality of honey?
Correct
Explanation
Quality of honey depends upon the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection.
Incorrect
Explanation
Quality of honey depends upon the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection.
-
Question 129 of 135
129. Question
- Which of these are the useful products of honey?
Correct
Explanation
Honey bees are used in the production of honey and bee wax. Other useful products obtained from honey bees are bee pollen, royal jelly, propolis and bee venom.
Incorrect
Explanation
Honey bees are used in the production of honey and bee wax. Other useful products obtained from honey bees are bee pollen, royal jelly, propolis and bee venom.
-
Question 130 of 135
130. Question
- Which of the following is not present in honey?
Correct
Explanation
Honey is a sweet, viscous, edible natural food product. Dextrose and sucrose gives sweet taste to the honey. It also contains amino acids, B-complex vitamins, ascorbic acid, and minerals. Formic acid is a preservative in honey. Invertase is an enzyme present in honey.
Incorrect
Explanation
Honey is a sweet, viscous, edible natural food product. Dextrose and sucrose gives sweet taste to the honey. It also contains amino acids, B-complex vitamins, ascorbic acid, and minerals. Formic acid is a preservative in honey. Invertase is an enzyme present in honey.
-
Question 131 of 135
131. Question
- Which of this acid is used as a preservative in honey?
Correct
Explanation
Formic acid is a preservative in honey.
Incorrect
Explanation
Formic acid is a preservative in honey.
-
Question 132 of 135
132. Question
- Which of this enzyme is present in honey?
Correct
Explanation
Invertase is an enzyme present in honey.
Incorrect
Explanation
Invertase is an enzyme present in honey.
-
Question 133 of 135
133. Question
- What are the uses of honey?
Correct
Explanation
Uses of Honey
- Honey has an antiseptic and antibacterial property. It is a blood purifier.
- It helps in building up of hemoglobin content in the blood.
- It is used in Ayurvedic and Unani system of medicines.
- It prevents cough, cold, fever and relieves sore throat.
- It is a remedy for ulcers of tongue, stomach and intestine.
- It enhances digestion and appetite.
Incorrect
Explanation
Uses of Honey
- Honey has an antiseptic and antibacterial property. It is a blood purifier.
- It helps in building up of hemoglobin content in the blood.
- It is used in Ayurvedic and Unani system of medicines.
- It prevents cough, cold, fever and relieves sore throat.
- It is a remedy for ulcers of tongue, stomach and intestine.
- It enhances digestion and appetite.
-
Question 134 of 135
134. Question
- How many calories does one kilogram of honey contain?
Correct
Explanation
One kilogram of honey contains 3200 calories and is an energy rich food.
Incorrect
Explanation
One kilogram of honey contains 3200 calories and is an energy rich food.
-
Question 135 of 135
135. Question
- What is the measure of total life time collection of honey by an average bee?
Correct
Explanation
Honey bee visits 50 to 100 flowers during a collection trip. Average bee will make only 1/12th of a teaspoon of honey in its lifetime.
Incorrect
Explanation
Honey bee visits 50 to 100 flowers during a collection trip. Average bee will make only 1/12th of a teaspoon of honey in its lifetime.
Leaderboard: Economic Biology Online Test 9th Science Lesson 23 Questions in English
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||